
When the file system has been mounted, it is possible to unmount it using the umount command (without an *). How Do I Unmount And Remove Filesystem In Linux? Credit:
WIPEFS EXAMPLE HOW TO
xfs_growfs can be used to grow it further if you need to (see section 6 for more information on how to use xfs_growfs). Wipefs -a must be set up if erasing is to occur. The rmfs command can be used to delete old file systems from a computer. For example, to force unmount the /dev/sdb1 file system, type the following command:
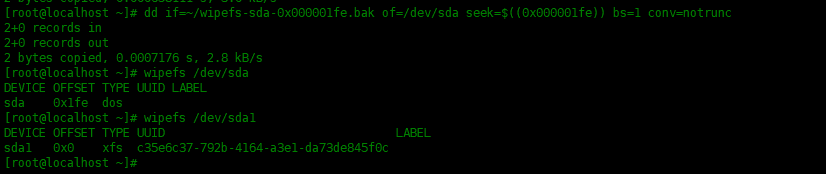
If the file system is in use, you may need to use the -l flag to force unmount it. For example, to unmount the /dev/sdb1 file system, type the following command: To unmount a file system, use the umount command. +Restores an ext2 signature from the backup file ~/ file systems in Linux can be unmounted via the command line. Restores ext2 signature from the backup file ~/wipefs-sdb-0x00000438.bak. More than one type -94,7 +95,7 Erases all signatures from the device /dev/sdb and creates a signature backupįile ~/wipefs-sdb-.bak for each signature. Limit the set of printed or erased signatures. +Suppress any messages after a successful signature wipe. Suppress output messages after successful signature wipe.


Encode all potentially unsafĬharacters of a string to the corresponding hex value prefixed by '\\x'. "K" has the same meaning as "KiB"), or the -77,7 +78,7 Print out in parsable instead of printable format. Suffixes KiB (=1024), MiB (=1024*1024), and so on for GiB, TiB, PiB, EiB, ZiB and YiB The \fIoffset\fR argument may be followed by the multiplicative It is possible to specify multiple \fB-o\fR options. The \fIoffset\fR number may include a "0x" prefix then the number will be Specify the location (in bytes) of the signature which should be erased from theĭevice. +order to erase a partition-table signature on a block device.ĭisplay help text and -66,7 +67,7 Causes everything to be done except for the write() call. order to erase the partition table on a block device. +For more details see the \fBEXAMPLES\fR section.įorce erasure, even if the filesystem is mounted. restricted with the \fB\-t\fP \fIlist\fP option.Ĭreate a signature backup to the file $HOME/wipefs-.bak. +For this the option \fB\-\-force\fR is required.Įrase all available signatures. +does not erase nested partition tables on non-whole disk devices. does not erase nested partition tables on non-whole disk devices. +When option \fB-a\fR is used, all magic strings that are visible for libblkid are When used with option \fB-a\fR, all magic strings that are visible for libblkid are +table will still be visible because of another magic string on another offset. +that after a \fBwipefs -o \fIoffset\fR the same filesystem or partition table will still be visible by another magic string on another offset. that after \fBwipefs -o \fIoffset\fR the same filesystem or partition Is not scanned for additional magic strings for the same filesystem. +Note that some filesystems and some partition tables store more magic strings onĬommand lists only the first offset where a magic string has been detected. Note that some filesystems or some partition tables store more magic strings on +calls the BLKRRPART ioctl when it has erased a partition-table signature calls BLKRRPART ioctl when erase partition table to inform kernel about the change. +When used without any options, \fBwipefs\fR lists all visible filesystemsĪnd the offsets of their basic signatures. When used without options \fB-a\fR or \fB-o\fR, it lists all visible filesystems SH -20,41 +20,42 to make the signatures invisible for libblkid.ĭoes not erase the filesystem itself nor any other data from the device.

+.TH WIPEFS 8 "December 2014" "util-linux" "System Administration" TH WIPEFS 8 "October 2009" "util-linux" "System Administration" \" This file may be copied under the terms of the GNU Public License.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
